Balance Sheet Template: Easy Solutions for Financial Tracking [+Free Download]

You’ve probably heard that half of all small businesses fail during the first five years. The question is: how do you avoid their fate? How can you predict and resolve financial issues before they collapse your business? Have a balance sheet.
The balance sheet is essentially a financial statement that captures all assets and liabilities of an organization at a specific point in time. Your balance sheet presents and helps you gain insight into:
- What your company owns as well as what it owes
- How much has been invested into your company
- What is your business’s net worth
Creating a comprehensive balance sheet can seem like a daunting task, but worry not! Below you will find all you need to understand:
- How do balance sheets work , why they are so important, what tools you need to work around it (for example, the best accounting software)?
- Can you learn how to read a balance sheet (and actually understand it)?
- How to create your own based on a simple balance sheet template?
What is the Purpose of a Balance Sheet?
Mainly, balance sheets are created for the purpose of reviewing the company’s financial status. Among other things, this can be useful if you want to:
- Analyze your business growth. A great balance sheet will have details of the current and previous years. It makes it easy to monitor the growth of your business.
- Mitigate growing concerns on time. Many businesses do not realize that their business cannot stay afloat until it’s too late. If your assets to liabilities ratio is below 1:1, you should find ways to increase your revenue.
- Determine your creditworthiness. Banks and other lenders will use your balance sheet to evaluate if you qualify for additional credit. Positive net worth can get your credit application approved.
A Free Balance Sheet Template
If you want to grab a simple balance sheet template and use it right away, you’ve come to the right place. The template below comes with all essential financial ratios. Ideal to suit the needs of small business owners!
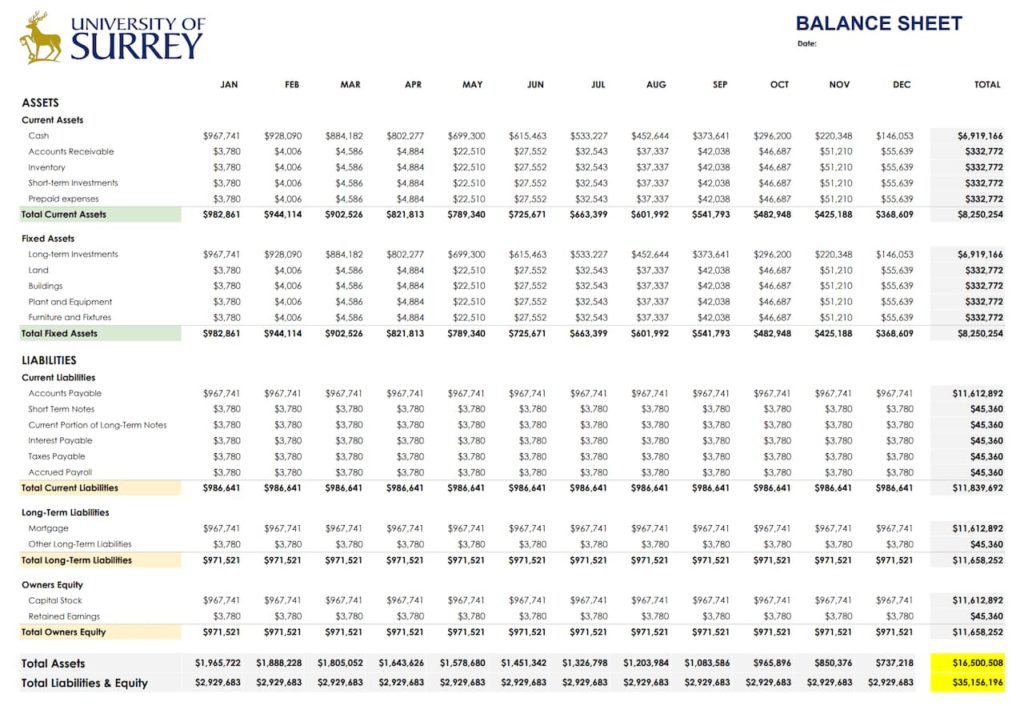
Note that this are View-only Google Sheets files. You cannot edit it directly. So make a local copy first and then edit the template. Before doing so, please make sure you’re signed in to your Google Account!
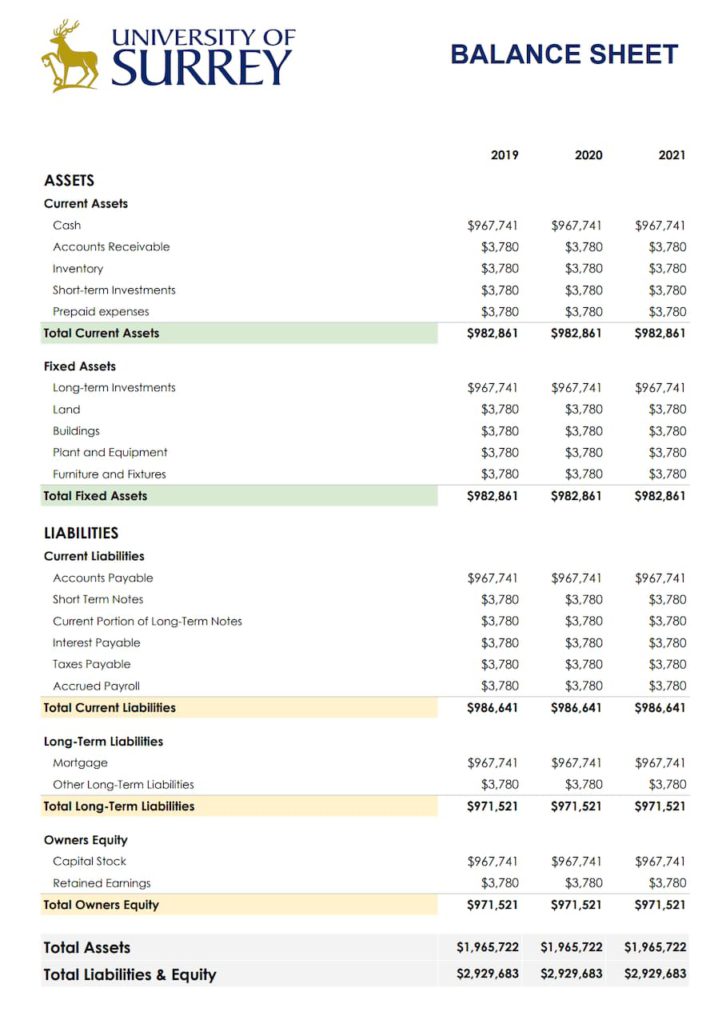
Now that you have the template to get you started. How do you fill it out? And what exactly does the balance sheet show, anyway? Worry not: we’ve got all the answers.
What Does the Balance Sheet Show
For you to better understand how to make a balance sheet, let’s look at the standard elements of the business balance sheet template.
Everhour is the top choice for small businesses and small to mid-size teams of 5 to 50 members, including professionals like software developers, marketers, designers, consultants, lawyers, you name it!
Seamlessly integrating with popular project management tools like Asana, Trello, and Jira, its user-friendly interface and customizable reports make it the ultimate time tracking solution for small and mid-size teams.
With dedicated support ensuring you receive timely assistance, our team is here to help you promptly and with a smile!
1. Current assets
These are items with a lifespan of less than a year and are easily convertible into cash. They show your business’s ability to finance daily business operations. Current assets include:

- Cash — This includes cash-in-hand, checks, and non-restricted bank accounts.
- Accounts receivables — This is money owed to your business, such as outstanding invoices.
- Inventory — Inventory includes finished products, work-in-progress goods, and raw materials.
- Prepaid Expenses — These are costs that you have paid but not used, or simply, expenses paid in advance.
- Short-term Investments — These are safe assets that are easy to convert to cash, such as debt securities.
2. Fixed (long-term) assets
Fixed assets cannot bring in cash easily and are not disposed of within the accounting year. They show the business’s ability to fund future needs. Long-term assets may include:

- Long-Term Investments — These are investments that you will hold for over a year, such as bonds and notes.
- Property Plant and Equipment (PPE) with the Depreciation Offset — They include machinery and equipment, real estate, fixtures and fittings, and furniture used to produce goods and services.
- Intangible Assets — These are assets that are not physical in nature, such as trademarks, patents, and intellectual property.
- Other assets, e.g. deferred income tax (this results from differences in income recognition between your business’s accounting methods and tax laws). Record an overpayment under “other assets”, and an underpayment under “long-term liabilities”.
3. Current liabilities
They are amounts that should be paid to creditors within a year using the current assets available. Current liabilities include:
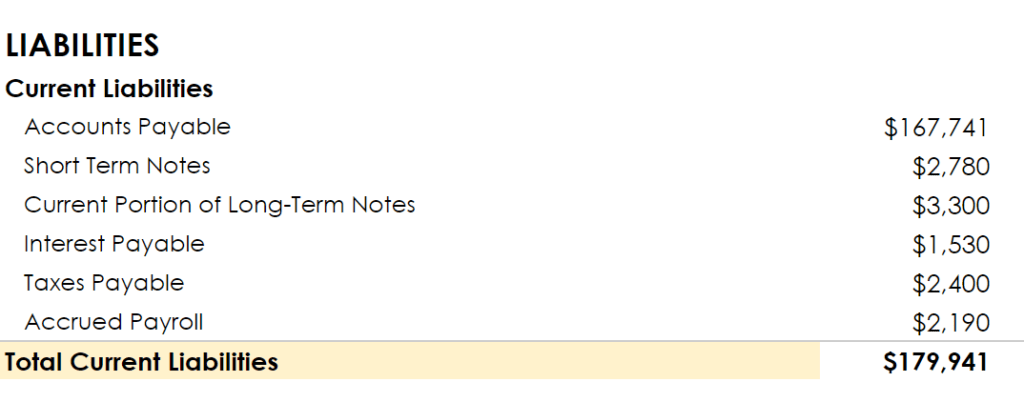
- Account Payables — These refer to the amounts you owe to suppliers.
- Short-term Loans — Are loans you take to support the business’s working capital needs and fall due within a year.
- Income Tax Payable — This is tax liability due to the government within the year.
- Accrued Salaries and Wages — Salaries that have been earned by your employees but not paid.
- Unearned Revenue — This is money you have received but are yet to deliver the goods or services.
- Current Portion of Long-term Debt — Add any loan principal that falls due within the year.
4. Long-term liabilities
This section includes obligations that are not due within your business’s operating cycle or in the next year. They show the business’s capital structure and its debt-to-equity ratio.

5. Owner’s equity
This section shows what you own. It’s the amounts that are left over after the liabilities are subtracted from the assets. Owner’s equity consists of:

- Owner’s Investment — This is your capital contribution to the company. It can include shareholder’s investments.
- Retained Earnings — These are net earnings reinvested back into the business instead of paying out as dividends.
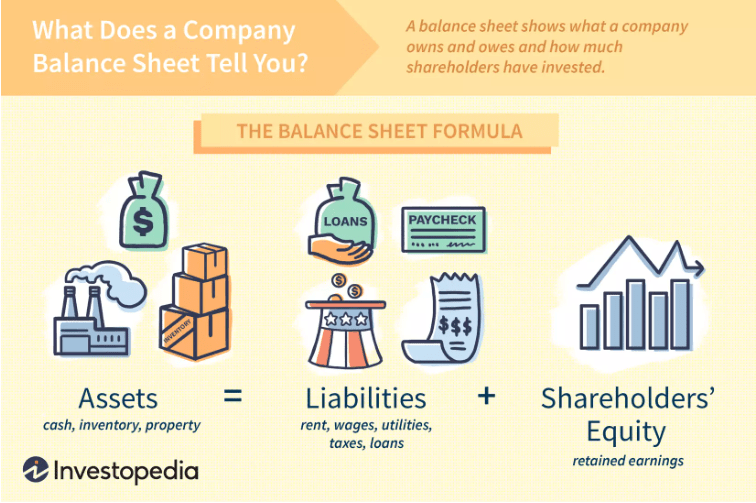
Here you have it: a summary of all the standard balance sheet elements. At its core, it’s actually pretty simple: assets on one side, liabilities + owner’s equity on the other side, balancing out.
Here’s a handy visualization by Investopedia:
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How do you know if a balance sheet is correct?
Your balance sheet is right when the sum of the assets equals the total liabilities and equity. -
Is a balance sheet the same as an income statement?
No, a balance sheet lists the assets, obligations, and owner’s equity of your venture while an income statement indicates the total revenues and expenses, and reports a net profit or loss. -
What is a classified balance sheet?
It is simply a more detailed and in-depth version of a balance sheet. It categorizes your business’s assets, liabilities, and equity into further classifications of accounts and contains subtotals for each category.
The Bottom Line
Ensuring your balance sheet is well done will help you to always know the financial position of your business. Consequently, it will be easier for you to make major decisions in an informed, rational way.
Feel that you needed one yesterday? Get started today with our hassle-free balance sheet template!
