Difference Between Bi-Weekly and Semi-Monthly Pay Explained [2024]

When it comes to payroll, the terms “bi-weekly” and “semi-monthly” are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to two distinct payment schedules. This can lead to confusion for both employers and employees alike. Understanding the difference between bi-weekly and semi-monthly is crucial for making informed decisions about payroll management, financial planning, and overall organizational efficiency.
In this article, we’ll break down what each term means, explore the advantages and disadvantages of both bi-weekly and semi-monthly pay schedules, and help you determine which option might be best for your organization or personal financial needs. This article will provide you with the clarity you need. Let’s dive into the details and clear up the confusion once and for all.
What is Bi-Weekly Pay?
Bi-weekly pay is a payroll schedule where employees receive paychecks every two weeks. Under this system, there are typically 26 pay periods in a year, meaning employees get paid twice a month for most months, with two months receiving three paychecks.
✅ Pros of bi-weekly pay
- Consistency: Employees receive paychecks regularly, which can make budgeting easier. Knowing that you’ll get paid every two weeks helps in planning expenses and managing cash flow.
- Additional paychecks: Since there are 26 pay periods in a year, employees receive two extra paychecks compared to a semi-monthly schedule. These “extra” paychecks in the two months with three paydays can provide a financial boost for employees.
- Simplified overtime calculations: For employers, calculating overtime can be simpler under a bi-weekly pay schedule, especially in industries where employees are eligible for overtime. Overtime is typically calculated weekly, so aligning the pay schedule with a weekly cycle can streamline payroll processing.
❌ Cons of bi-weekly pay
- Variable payday: Unlike semi-monthly pay, where paydays are fixed (e.g., the 1st and 15th of every month), bi-weekly paydays can vary, falling on different dates each month. This can make it slightly more challenging for employees to plan their finances around specific payment dates.
- Increased payroll processing: Employers must process payroll more frequently—26 times a year compared to 24 with semi-monthly pay. This can lead to higher administrative costs and time spent on payroll tasks.
- Potential for confusion: Employees who are not familiar with the bi-weekly pay schedule might get confused by the varying pay dates and the two months with an extra paycheck, complicating their budgeting efforts.
Managing these complexities can be a breeze with the right tools in place. Everhour, a top-tier time tracker and one of the best billable trackers out there, simplifies payroll processing, whether you’re working with bi-weekly or semi-monthly schedules! Seamlessly integrating with popular PM tools, its user-friendly interface and customizable reports make it the ultimate time tracking solution. With dedicated support, our team is here to help you promptly and with a smile!
What is Semi-Monthly Pay?
Semi-monthly pay is a payroll schedule where employees are paid twice a month, typically on fixed dates such as the 1st and the 15th, or the 15th and the last day of the month. This results in 24 pay periods for a year.
✅ Pros of semi-monthly pay
- Fixed pay dates: Employees receive their paychecks on the same two dates every month, making it easier to plan and budget. This consistency can help with managing bills and expenses that are also due on specific dates.
- Easier alignment with monthly expenses: Since many bills and financial obligations are due monthly, receiving pay on a semi-monthly schedule can make it simpler for employees to align their income with their monthly expenses.
- Lower payroll processing frequency: For employers, processing payroll only 24 times a year can reduce administrative workload compared to bi-weekly pay, which requires 26 payroll runs.
❌ Cons of semi-monthly pay
- Variable paycheck amounts for hourly employees: For hourly employees, the number of workdays in a semi-monthly pay period can vary, leading to fluctuations in paycheck amounts. This inconsistency can make budgeting more challenging for those who rely on a steady income.
- Complex overtime calculations: Calculating overtime can be more complicated under a semi-monthly schedule, as it doesn’t align neatly with the weekly overtime thresholds that are often used in labor laws. This can create additional work for payroll departments.
- Longer gaps between paychecks: In a semi-monthly pay schedule, there can be longer gaps between paychecks, especially in months with 31 days, potentially making it harder for some employees to manage their cash flow.
Bi-Weekly vs. Semi-Monthly Pay Schedules
When deciding between bi-weekly vs semi-monthly pay schedules, it’s essential to understand how each impacts both employers and employees. Though both methods ensure employees are paid twice a month, the timing and structure of payments can vary significantly, leading to different experiences in cash flow, budgeting, and payroll management.
⌛ Payment frequency and dates
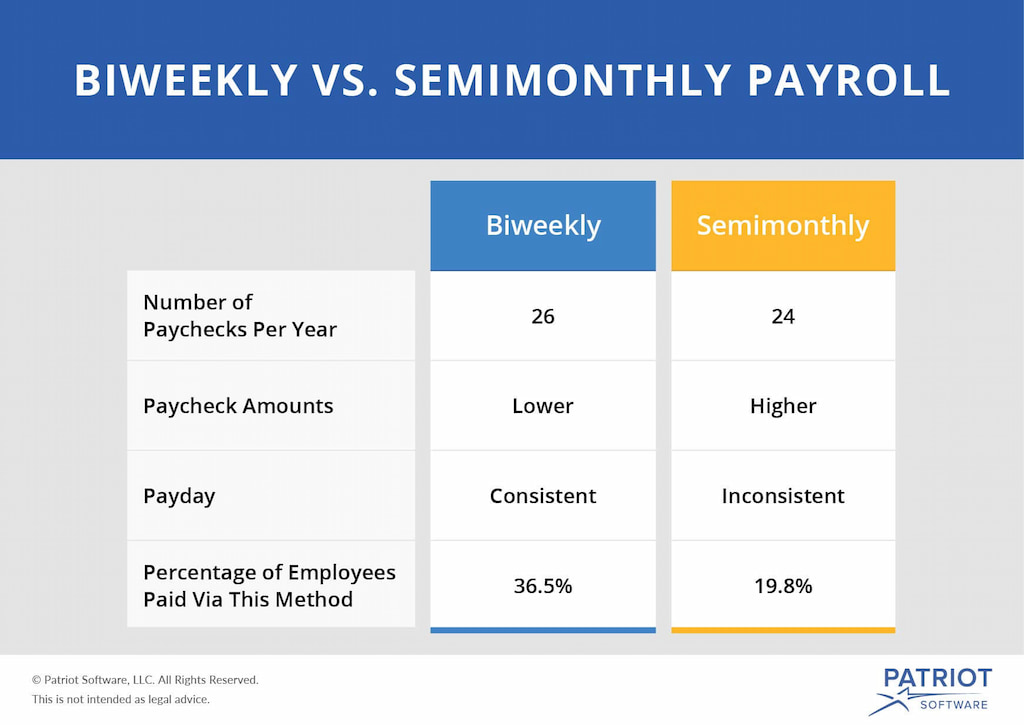
- Bi-weekly pay: Employees receive paychecks every two weeks, resulting in 26 pay periods in a year. The payment dates shift slightly each month, as the pay is based on a consistent 14-day cycle. This can lead to situations where employees receive three paychecks in a single month, typically twice a year.
- Semi-monthly pay: Employees are paid twice a month, usually on fixed dates like the 1st and 15th, or 15th and last day of the month, totaling 24 pay periods in a year. These dates remain consistent, providing predictability, but the length of each pay period can vary between 13 to 16 days depending on the month.
😩 Impact on employees
Bi-weekly pay
- Pros: The consistent two-week cycle aligns well with hourly work schedules, making it easier to calculate overtime and manage cash flow. Additionally, the occasional “extra” paycheck in some months can be beneficial for employees.
- Cons: The shifting payday can make it difficult to align paychecks with monthly bills, potentially leading to budgeting challenges.
Semi-monthly pay
- Pros: Fixed paydays provide employees with predictability, making it easier to manage monthly expenses and bills. This schedule aligns well with salaried employees who have a consistent workload each month.
- Cons: For hourly employees, varying workdays in each pay period can result in fluctuating paychecks. The longer gaps between paydays, especially during longer months, may also pose cash flow challenges.
👨💼 Impact on employers
Bi-weekly pay
- Pros: Aligns well with weekly timesheets, making payroll processing straightforward for both salaried and hourly employees. It’s also simpler to calculate overtime for hourly workers, reducing potential errors.
- Cons: With 26 pay periods, payroll processing is more frequent, leading to higher administrative costs and more time spent on payroll management.
Semi-monthly pay
- Pros: Fewer payroll cycles (24 vs. 26) can reduce administrative burden and costs. This method also simplifies financial planning and aligns well with monthly financial reporting.
- Cons: Payroll calculations can become more complex, especially for hourly employees and those eligible for overtime. The variation in the number of workdays per period can complicate payroll processing.
💸 Cash flow considerations
- Bi-weekly pay: Employees benefit from more frequent paydays, which can aid in cash flow management. However, the varying payday dates may require extra attention to budget effectively, particularly in months with three paychecks.
- Semi-monthly pay: The consistent schedule of semi-monthly pay is easier for long-term financial planning but can lead to challenges if an employee’s cash flow is tight, especially during longer months when the gap between paychecks is greater.
Choosing between bi-weekly and semi-monthly pay schedules depends on the specific needs of the organization and its workforce. Employers should consider the nature of their workforce (hourly vs. salaried), the complexity of payroll processing, and the preferences of their employees when making this decision. Both methods have their advantages and potential drawbacks, so finding the right balance is key to ensuring smooth operations and satisfied employees.
Exploring Other Payroll Schedules
In addition to bi-weekly and semi-monthly pay schedules, there are several other payroll schedules that organizations might consider, depending on their operational needs and workforce preferences. Each schedule has its own set of benefits and challenges, which can impact both employers and employees in different ways.
Weekly payroll
Weekly payroll involves paying employees once a week, typically on the same day, such as every Friday. This schedule is common in industries with hourly workers, like retail, construction, and hospitality, where employees may rely on a steady flow of income to manage their weekly expenses.
✅ Pros
- Frequent paychecks: Employees receive their earnings more regularly, which can be beneficial for budgeting and managing living expenses.
- Employee satisfaction: A consistent cash flow can lead to higher employee satisfaction, particularly for those who prefer more immediate access to their wages.
- Simple calculations: Overtime and variable pay are easier to calculate on a weekly basis, reducing the risk of payroll errors.
❌ Cons
- Administrative burden: Processing payroll weekly increases the administrative workload and may require additional resources or automation to manage effectively.
- Higher costs: More frequent payroll processing can lead to higher costs for businesses, including bank fees and payroll service charges.
Monthly payroll
Monthly payroll is when employees are paid once a month, typically at the end of the month. This schedule is less common in the U.S. but is widely used in some European countries and other parts of the world.
✅ Pros
- Reduced administrative work: With only 12 pay periods per year, the administrative burden is significantly reduced, allowing payroll teams to focus on other tasks.
- Cost-effective: Fewer pay periods mean lower processing costs, making it a more cost-effective option for employers.
❌ Cons
- Budgeting challenges: Employees may find it challenging to manage their finances with only one paycheck per month, leading to potential cash flow issues.
- Lower employee satisfaction: The long gap between paychecks can be frustrating for employees, potentially affecting morale and retention.
Daily payroll
Daily payroll is an emerging trend where employees can access their earnings on a daily basis, often facilitated by financial technology platforms. This method is particularly appealing in the gig economy and for employees who prefer or need immediate access to their wages.
✅ Pros
- Immediate access: Employees can access their earnings almost instantly, which can be a significant advantage for those with urgent financial needs.
- Increased flexibility: Daily payroll offers greater flexibility and can be an attractive benefit for gig workers and hourly employees.
❌ Cons
- Complexity: Managing daily payroll can be complex and may require advanced payroll software to handle the frequent transactions and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
- Potential for mismanagement: Without careful budgeting, employees may overspend and find themselves short on funds later in the month.
Simplifying Payroll with Everhour
Choosing between semi-monthly vs bi-weekly pay schedules is a critical decision that impacts both employers and employees. Bi-weekly pay offers consistent paycheck amounts and is often preferred for hourly workers, but it requires more frequent payroll runs. Semi-monthly pay, on the other hand, provides predictability with fixed pay dates, which can simplify financial planning but may complicate payroll calculations for varying work periods.
For businesses aiming to streamline their payroll process, integrating a time-tracking tool like Everhour can be invaluable. Everhour seamlessly syncs with your payroll system, making it easier to manage and track employee hours accurately, whether you choose bi-weekly or semi-monthly pay. This ensures that your payroll is not only accurate but also efficient, freeing up time to focus on other aspects of your business.

All-in-one time management system for your team
Estimate tasks, set budgets, customize reports – direct in your project management tool.
✔️ Asana time tracking
✔️ Trello time tracking
✔️ Basecamp time tracking
✔️ Jira time tracking
✔️ GitHub time tracking
✔️ ClickUp time tracking
✔️ Monday time tracking
