Navigating Rotating Shift Work: A Comprehensive Guide for Employers and Employees

In today’s rapidly evolving and interconnected world, numerous sectors operate 24/7 to fulfill customer needs and enhance efficiency. This trend has given rise to the prevalent practice of shift rotation, a scheduling approach involving employees working varying shifts at different intervals.
In this blog post, we will explore the concept of rotating shift work, its various types, advantages, disadvantages, and its impact on employee health. Additionally, we will provide tips for effectively managing rotating shifts and present insights into industries that commonly implement this scheduling approach.
What is a Rotating Shift Work?
Rotating shift work involves scheduling employees in blocks of time that change periodically, typically weekly or monthly.
This scheduling system ensures continuous operation and allows employers to cover various shifts, including day, evening, and night shifts.
This type of shift schedule is commonly utilized by businesses that require round-the-clock operations to meet their operational demands effectively.
Instead of assigning specific employees to work only during unpopular hours, the employer opts for a rotation system, distributing the burden of those shifts equally among the team. As a result, each employee takes turns working both favorable and challenging shifts.
For example, a night-shift nurse who has a rotating schedule. She works three days a week, from 7 PM to 7:00 AM. However, the specific days she works each week are not fixed. She can work Sunday, Monday, and Tuesday one week, then Thursday, Friday, and Saturday the next. This rotating shift pattern allows for variety and flexibility in her work schedule.
Shifts by Everhour provides an intuitive solution for managing employee schedules with ease. From flexible scheduling options to mobile accessibility, it’s the ideal solution for optimizing workforce management in any industry.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics provides statistical data on the primary reasons for working non-daytime schedules categorized by gender and type of shift.
Types of Rotating Shifts and Patterns
DuPont Shift Schedule
The DuPont Shift Schedule is a widely used shift schedule in various industries. It was developed by the DuPont Corporation in the early 20th century to address the challenges of providing continuous operations while ensuring adequate rest and sufficient workforce coverage.
The DuPont Shift Schedule typically consists of a repeating cycle of 12-hour shifts, covering 24 hours a day and seven days a week. It follows a specific pattern of day shifts, night shifts, and rest days for employees. The schedule is structured to ensure that employees have sufficient time off between shifts, minimizing fatigue and improving overall work-life balance.
The specific rotation pattern may vary depending on the organization’s requirements, but the typical scheduling cycle for the DuPont shift schedule sequence is:
4 night shifts > 3 days off > 3 day shifts > 1 day off > 3 night shifts > 3 days off > 4 days shifts > 7 days off.
The DuPont schedule offers an appealing aspect as employees enjoy a consecutive 7-day break, allowing them to rest and rejuvenate before returning to work. However, it also presents challenges, primarily because the shifts are often long and there is only one day off in the middle of a lengthy stretch of shifts. Furthermore, some weeks may require employees to work well beyond the standard 40-hour workweek, which can be demanding.
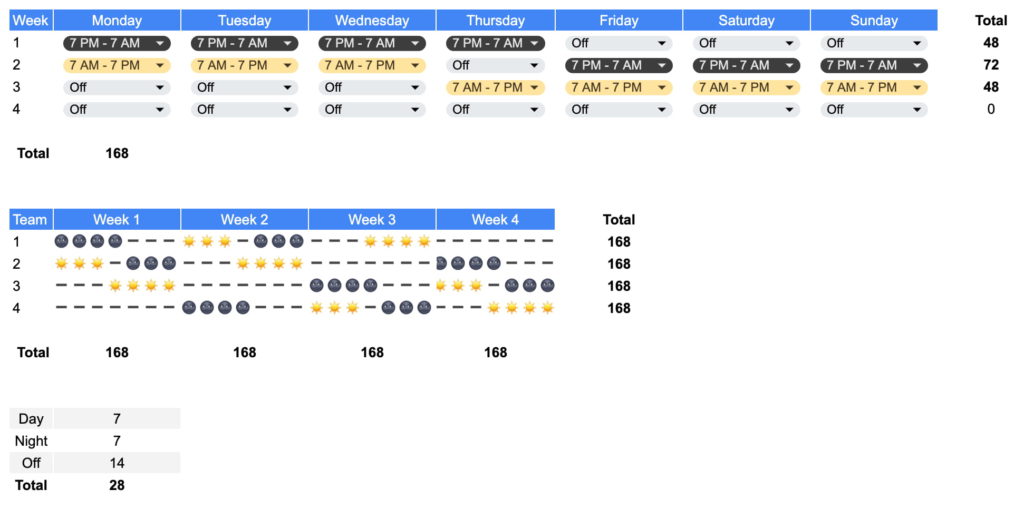
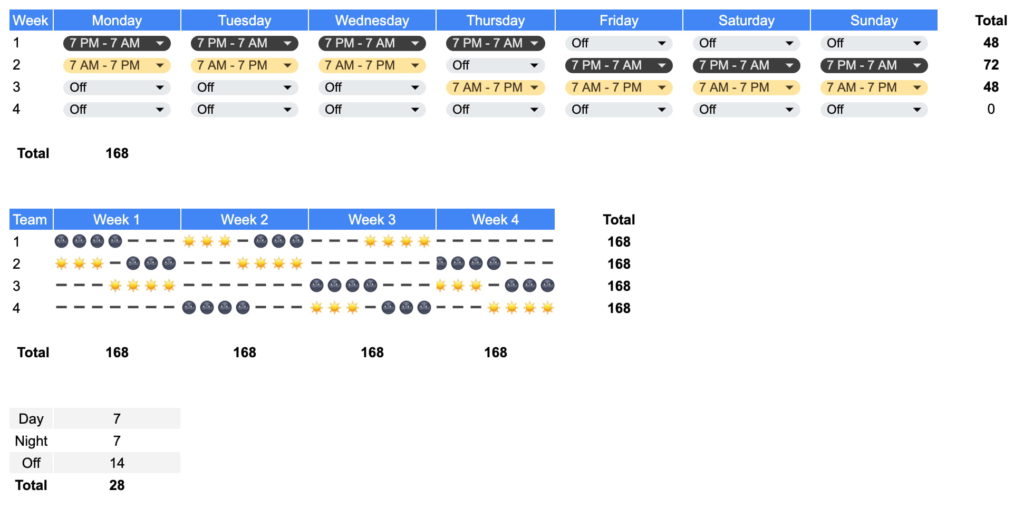
Southern Swing Schedule
The Southern swing shift schedule uses three 8-hour shifts rotating on a 28-day cycle. Companies use four teams that work each shift throughout the month according to the following schedule:
7 day shifts > 2 days off > 7 swing shifts > 2 day off > 7 night shifts > 3 days off.
Swing shifts, also known as second shifts, are work schedules that typically occur in the afternoon or evening, overlapping with both the day and night shifts. The name “swing” comes from the idea that these shifts swing or shift between the day and night shifts. Employees working swing shifts start later in the day, work through the evening, and end their shifts during the night.
The Southern swing schedule offers the advantage of 8-hour shifts, which can be more manageable compared to longer 12-hour shifts. However, one potential challenge with this schedule is that employees work 7 consecutive days, and some individuals may require time to adapt to this continuous work pattern.
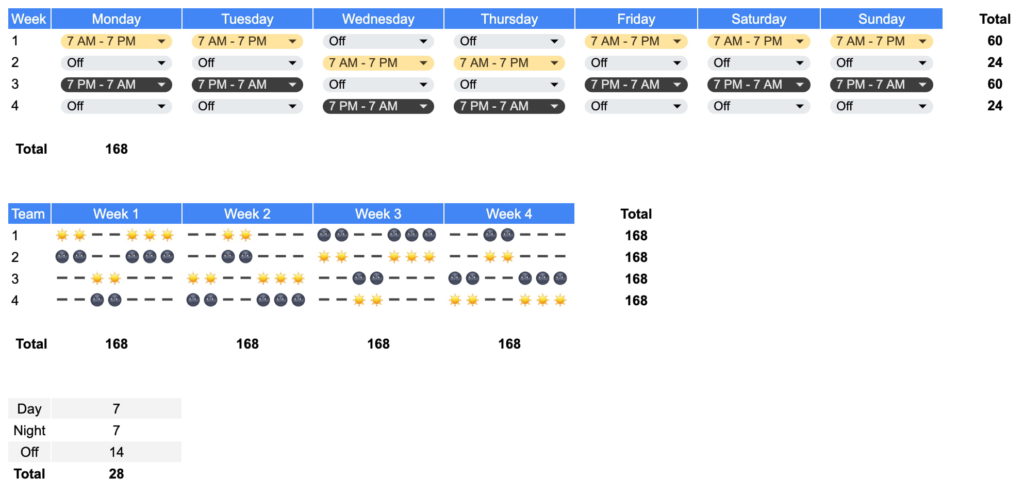
Pitman Shift Schedule (or 2-3-2 schedule)
The Pitman schedule runs on a two-week cycle:
2 shifts > 2 days off > 3 shifts > 2 days off > 2 shifts > 3 days off.
Two teams are assigned day shifts while the other two are assigned night shifts. On any given day, one team is on the day shift, one team is on the night shift, and two teams are off.
Using this rotating schedule, employees get every other weekend off, which provides a measure of normalcy for employees to spend time with family or complete personal tasks.
Benefits of Rotating Shifts
Rotating shifts can offer several advantages for both employers and employees. One significant benefit is enhanced coverage, allowing businesses to operate around the clock, ensuring continuous productivity and service provision. For industries that require 24/7 operations, such as healthcare, manufacturing, and public safety, rotating shifts are essential to meet customer demands at all hours. This increased coverage can lead to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty, which is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in today’s global market.
From an employee perspective, rotating shifts can provide greater schedule flexibility and variety. Some individuals may prefer a rotating schedule as it allows them to experience different shifts, work with diverse teams, and enjoy varied days off. This can lead to a more engaging work environment, reducing monotony and increasing job satisfaction. Employees may also appreciate the opportunity to schedule appointments or attend personal commitments during non-traditional working hours, thus achieving a better work-life balance.
Disadvantages of Rotating Shifts
Despite the benefits, rotating shifts also come with their share of challenges. One primary concern is the potential impact on employees’ health and well-being. Constantly changing sleep patterns and disrupted circadian rhythms can lead to sleep disturbances and fatigue. Long-term exposure to rotating shifts has been associated with various health issues, such as increased risk of cardiovascular disease, digestive problems, and mood disorders.
Moreover, rotating shifts can pose difficulties in maintaining stable social and family relationships. Employees working rotating shifts often struggle to sync their personal lives with their ever-changing work schedules, leading to feelings of isolation and difficulty in making social plans. The lack of consistent routines can also make it challenging to engage in regular physical and recreational activities, which are vital for overall well-being.
Another disadvantage is the potential negative impact on work performance and productivity. Sleep deprivation and fatigue can impair cognitive function, decision-making, and reaction times, increasing the risk of accidents and errors on the job. Reduced concentration and alertness during certain shifts may also lead to decreased productivity, affecting overall organizational efficiency.
How to Schedule Employees for Rotating Shifts
Scheduling employees for rotating shifts requires careful planning and consideration of various factors to ensure smooth operations and employee well-being. Here are some key steps and tips to effectively schedule employees for rotating shifts:
1. Understand Business Needs: Before creating the schedule, assess your business’s requirements, including peak hours, customer demand, and necessary coverage. Consider the number of employees needed for each shift and the skills required for different time slots.
2. Define Rotating Shift Patterns: Determine the rotating shift patterns that align with your business needs. Choose a pattern that suits your industry and allows for adequate rest between shifts.
3. Establish Scheduling Rules: Set clear rules for scheduling, such as the maximum number of consecutive shifts, the minimum rest period between shifts, and the process for requesting shift swaps or time-off. Clearly communicate these rules to all employees to avoid confusion and ensure compliance.
4. Consider Employee Preferences: Take into account employee preferences and availability when creating the schedule. Some employees may have specific time constraints or personal commitments that need to be accommodated. Flexibility in scheduling can increase employee satisfaction and reduce turnover.
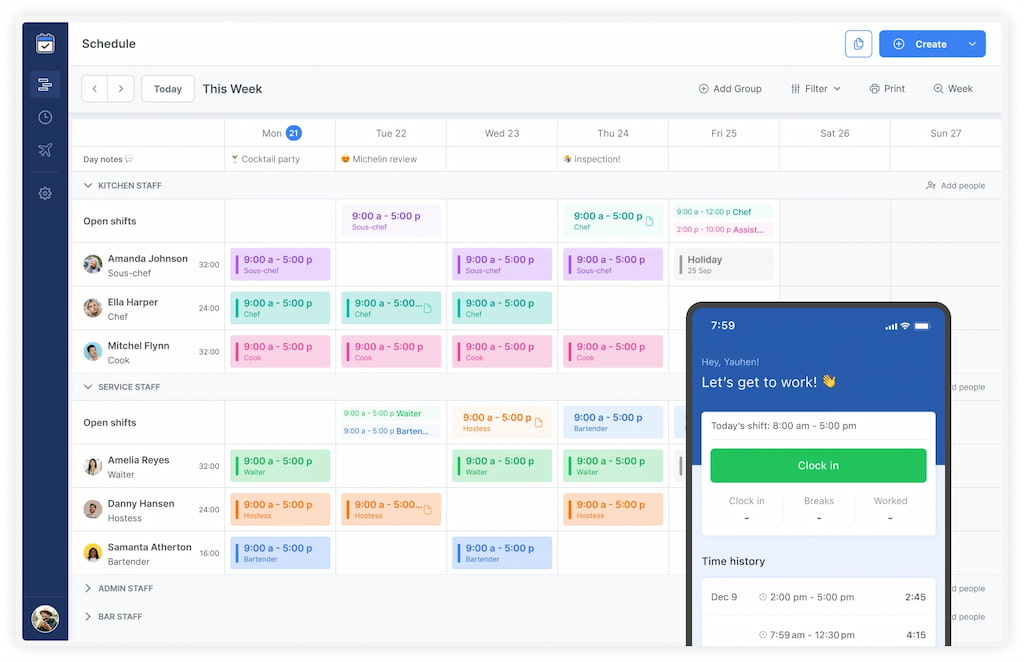
5. Utilize Scheduling Software: Consider using scheduling software (like Shifts by Everhour) or apps to streamline the process and automate shift rotations. These tools can help avoid scheduling conflicts, track employee availability, and notify employees of their upcoming shifts.
6. Monitor Overtime and Fatigue: Keep track of employees’ work hours to prevent excessive overtime and fatigue. Schedule rest days and breaks strategically to allow sufficient time for employees to rest and recharge.
7. Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review the rotating shift schedule and gather feedback from employees to identify any issues or areas for improvement. Be open to making adjustments based on feedback and changing business needs.
8. Provide Support and Resources: Offer support and resources to employees who may be struggling with the challenges of rotating shifts. This can include access to wellness programs, stress management workshops, and resources for improving sleep hygiene.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rotating shifts offer both advantages and disadvantages for businesses and their employees. While they ensure continuous coverage and schedule flexibility, they can also lead to health issues, disrupt personal lives, and impact work performance.
To mitigate the drawbacks, employers should implement strategies such as providing adequate rest periods between shifts, offering employee support programs, and actively involving employees in creating flexible and balanced schedules.
By carefully considering the needs of both the organization and its workforce, businesses can create a harmonious work environment that maximizes the benefits of rotating shifts while minimizing their potential drawbacks.
